
Primary Bronchogenic Carcinoma (LUNG CANCER). SHEN JIN The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical College. Outlook. 1. Pathologic Characteristics 2. Clinical Features 3. Imagine Manifestations 4. Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis. Pathologic Characteristics. 1.Difinition

tilden + Follow
Download PresentationAn Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.

Lung Cancer What Is Lung Cancer? Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death for men and women. It is also the most preventable form of cancer. Tobacco use accounts for 87% of lung cancers. There are two major types of lung cancer: 1. Non-small cell lung cancer (87%)
1.05k views • 24 slides

Bronchogenic Carcinoma. Abstract. Brochogenic carcinoma is also called Lung cancer. It is a frequent and important neoplasm in both developed country and developing country. In recent years, It is reported that lung cancer is the leading fatal neoplasm of men and women.
2.47k views • 55 slides
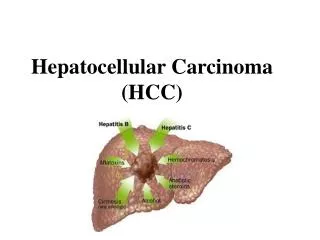
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). • Different types of cancer can behave very differently . For example , lung cancer and breast cancer are very different diseases . They grow at different rates and respond to
1.43k views • 25 slides
 ACC Cancer Plan" width="320px" />
ACC Cancer Plan" width="320px" />
ACC Cancer Plan . Lung Cancer . Best for last ?. F irst for last !. Prevention . Education. Access. ACC Lung Cancer . Education. Prevention . Access. ACC Lung Cancer . Tobacco and Disease: The 5 th Annual Lung Cancer Symposium. November, 2014.
707 views • 56 slides

Non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Non-small-cell lung carcinoma ( NSCLC ) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small cell lung carcinoma ( SCLC). As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small cell carcinoma.
758 views • 21 slides
Lung Cancer . By Erica Yellowknee Dec 27 2009. What cause lung cancer?. Smoking, passive smoking, asbestos fibbers, radon gas, familial predisposition, lung diseases, and air pollution cause lung cancer. The main causes is smoking. . Effects of lung cancer .
396 views • 7 slides

Tha role of FDG-PET for Mediastinal Staging in Primary Lung Cancer. Osman Eroğlu, Sedat Ziyade, Alper Toker, Serhan Tanju , Sukru Dilege, Goksel Kalayc ı Istanbul Universty Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery. Mediastinal Evaluation in Lung Cancer. Non-invasive CT
444 views • 17 slides

Lung Cancer. By: Priyanka , Sonya, and Akshatha. Lung cancer is a cancer that forms in the tissues of the lung. Mostly in the cells lining the air passages. History and Origin. There are two types of cancer: Small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer
597 views • 10 slides
 Network Primary Care Cancer Education Programme" width="320px" />
Network Primary Care Cancer Education Programme" width="320px" />
Mount Vernon Cancer Network. Wednesday 29 th February 2012 Novotel, Stevenage. Mount Vernon Cancer Network Primary Care Cancer Education Programme. Recognising the Early Signs and Symptoms of Cancers Programme 1: Bowel, Ovarian, Oesophagogastric and Lung Cancers. Mount Vernon Cancer Network.
1.45k views • 127 slides
 Network Primary Care Cancer Education Programme" width="320px" />
Network Primary Care Cancer Education Programme" width="320px" />
Mount Vernon Cancer Network. Wednesday 21 st March 2012 Niland Centre, Bushey. Mount Vernon Cancer Network Primary Care Cancer Education Programme. Recognising the Early Signs and Symptoms of Cancers Programme 1: Bowel, Ovarian, Oesophagogastric and Lung Cancers. Mount Vernon Cancer Network.
1.57k views • 137 slides

Clinical Impression: BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA. Histopathologic image of small cell carcinoma of the lung. CT-guided core needle biopsy. H & E stain. Non-small cell lung carcinoma. 75% of lung cancer Grows and spreads more slowly than small cell Ca
225 views • 11 slides

Lung Cancer. By: Ashish , Andy, and Megan. Lung Cancer. What is Lung Cancer ? Lung Cancer is the most common type of cancer. Origins of Lung Cancer. What is the History/Origin of Lung Cancer ? Nearly nonexistent in the early 1900’s
796 views • 17 slides

Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Overview with Focus on Management. John M. Watkins, M.D. Medical University of South Carolina Department of Radiation Oncology. Background. Small Cell Lung Cancer 15-20% of primary lung neoplasms Decreasing incidence Classically large, central mass
949 views • 69 slides

Clinical Impression: BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA. Histopathologic image of small cell carcinoma of the lung. CT-guided core needle biopsy. H & E stain. Non-small cell lung carcinoma. 75% of lung cancer Grows and spreads more slowly than small cell Ca Types: Adenocarcinoma Squamous cell ca
332 views • 12 slides

Sequential vs. concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced non-small cell carcinoma. Background. Lung cancer remains leading cause of cancer death in UK 5 year survival 8% (all stages) Non-small cell lung cancer accounts for 80% of cases
311 views • 15 slides
Compass Medical provides Lung Cancer Treatment and Medical Tourism in Germany, Lung Cancer Surgery, Small Cell Lung Cancer and all types Lung Cancer Diagnosis.
146 views • 10 slides

CARCINOMA PANCREAS. EXOCRINE PANCREASE 5 TH MOST FREQUENT CAUSE OF CANCER DEATH PRECEDED BY LUNG,COLON,BREAST PROSTATE CANCER. CARCINOMA PANCREAS. 1.EPIDEMIOLOGY 2. PATHOGENESIS INCLUDING MOLECULAR LEVEL 3.PATHOLOGY GROSS MICROSCOPY 4. DIAGNOSIS 5. CLINICAL FEATURES
523 views • 45 slides

DNA diagnosis of lung cancer Patrick Willems GENDIA Antwerp, Belgium. Treatment of Lung Cancer. Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) chemotherapy radiation Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) surgery radiation chemotherapy targeted treatment immunotherapy.
723 views • 69 slides